Sarah Bhattacharjee
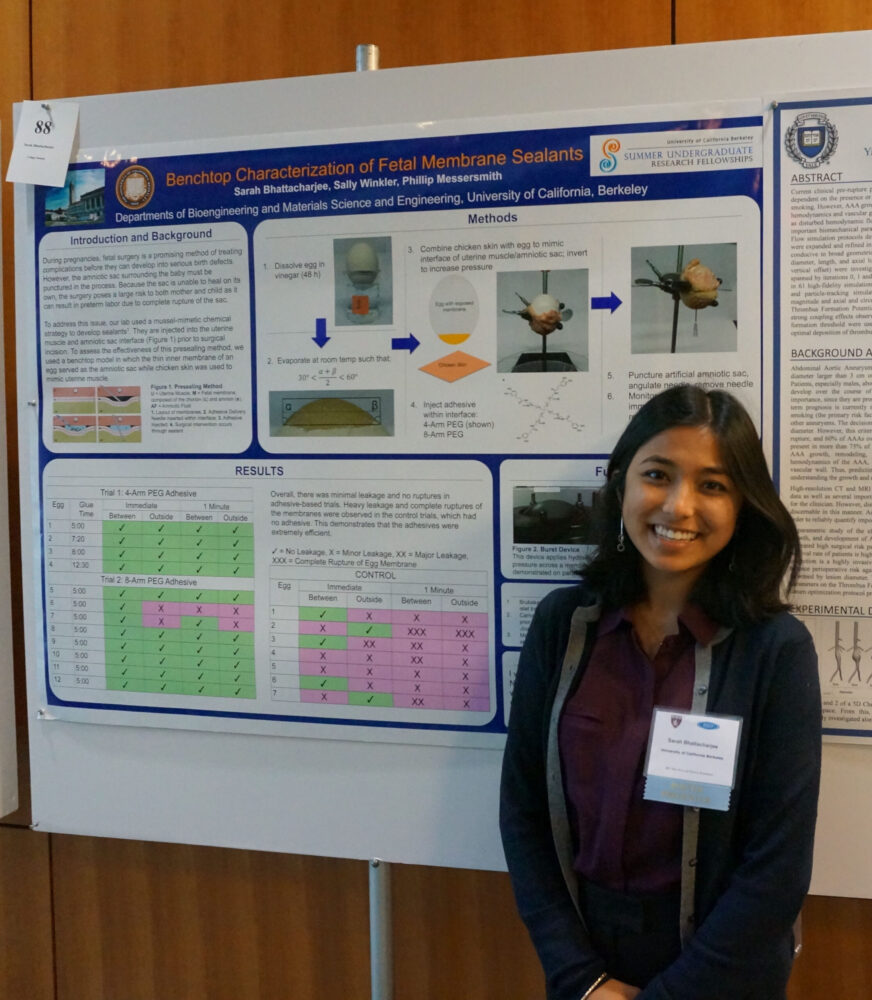
During pregnancy, complex birth defects can arise, and fetal surgery can correct or drastically ameliorate these conditions. The largest unmet need of the field is a method to seal the amniotic sac, as it does not heal following surgery and can rupture, leading to preterm birth. I hope to develop self-sealing needles and instrument sheaths to seal defects in the amniotic sac during and after surgery. Hopefully these new methods will help fetal surgery become a viable and safe option for growing families.
Freja Ekman

Efficient and versatile genome editing technologies, including CRISPR/Cas9, have the potential to treat disease on a genetic level. By inducing DNA double stranded breaks at targeted genomic locations, targeted nucleases can facilitate gene disruption via the introduction of random base insertions and deletions via non-homologous end joining. While many studies have developed methods for implementing these techniques, the treatment of nervous system disorders via genome editing has remained largely unexplored. One such disorder is Huntingtons disease (HD). HD is an autosomal-dominant disorder characterized by the progressive loss of striatal neurons […]
Sharon Feng

Genome editing is an emerging topic with immediate and significant implications in human health. Despite interest in therapeutic gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9, interactions between genome editing reagents and human cells remain poorly understood. Prior work in the Corn Lab identified how human cells integrate single stranded DNA into Cas9 cut sites. My project will build upon this work to establish how cells respond to other gene editing techniques, namely the integration of double stranded DNA into genomic DNA.
Ivonne Verduzco
Members of the superfamily Tipuloidea, commonly called craneflies, are the largest group of Diptera, or flies. There are currently 18,000 species known. While this group is an important player in most ecosystems, serving as general decomposers, predators, or crop pests, little is known about the relationships between cranefly families or genera. My research is aimed at deconstructing the uncertainty of these relationships. A phylogenetic hypothesis for this group will facilitate further studies of cranefly evolution and will help answer questions about diversification in this group. For example, why are there […]
Jazlyn Chong
CoQ is an essential molecule in the electron transport chain (ETC) which acts as an electron carrier to help generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the mitochondria. Therefore, without CoQ or under conditions of severe CoQ deficiency, the redox reactions required for efficient energy production are greatly hampered. The inordinately high levels of mitochondria in brown adipose tissue (BAT) also suggest that a CoQ deficiency could negatively and significantly impact the unique BAT function of thermoregulation through nonshivering thermogenesis. Defective BAT function could then lead to excess fat deposition, obesity, and […]
Tiffany Fung

Patients with central vision loss (scotoma) often rely on a location outside the scotoma for seeing, the preferred retinal locus (PRL). We investigated whether the development of a PRL in response to a simulated scotoma in normally sighted individuals is the result of oculomotor adaptation, as is the case in patients with a real scotoma. We used a gaze-contingent paradigm to occlude the central vision of normally sighted subjects while they performed a visual task.
Daniel Jong Hyun Choi

With advances in health care and changes in lifestyle, humans are living healthier, longer. As a result, there has been a dramatic increase in the incidence of age-related diseases such as Alzheimers and Parkinsons. Despite decades of study, the mechanisms driving neurodegenerative disease pathogenesis remain unknown and effective treatments elusive. Inflammation is a hallmark feature of neurodegeneration, suggesting that inflammatory responses could be both protective and harmful to tissue physiology. We are developing a small molecule paradigm of extracellular proteotoxicity that is amenable to high-throughput genomic studies. Our preliminary data […]
Kayleigh Cook

My project centers on epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) which are located in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. From previous studies, they have been shown to be potent vasodilators and though the receptor is not known, their mechanism is believed to rely on calcium activated potassium channels and the hyperpolarization of smooth muscle. In addition to vasodilation, EETs are known to help maintain cardiovascular homeostasis through anti-inflammatory effects and can protect against ischemia and hypertension. Discovering the receptors that control the potential benefits of EETs could lead to new therapeutic options […]
Alan Liu

The use of fossil fuels to produce fuels is leading to an increase in changes of global climate due to the large amount of carbon dioxide released. Fossil reserves are also becoming scarcer, so alternative energy sources such as those from biomass derived alcohols are becoming more important. It is known that some biomass derived alcohols, such as glycerol, can react with aldehydes and ketones to form acetals and ketals that are possible useful fuel additives. My research project will focus on probing the kinetics and mechanisms of the liquid […]
Leo Porter-Zasada

In this project, I will attempt to create a less expensive and more effective method to synthesize and separate chiral compounds in large quantities. Because a large percentage of biological molecules are chiral (i.e. they have non-superimposable mirror images), many bioactive and pharmaceutical compounds are also chiral, and separations and synthesis of these chiral compounds is a pivotal challenge in pharmaceutical research. To address this challenge, I aim to create an enantiopure chiral metalorganic framework (MOF) by introducing chiral additives during synthesis to induce bulk homochirality. Preliminary findings indicate this […]